Density-based intrinsic persistent homology and applications to time series analysis
XIMENA FERNANDEZ
Durham University
CENTRE FOR TOPOLOGICAL DATA ANALYSIS
Group Meeting - 19th November 2021
Density-based
intrinsic persistent homology
$\bullet$ Fernandez X., Borghini E., Mindlin G., Groisman P. Intrinsic persistent homology via density-based metric learning, 2021. arXiv:2012.07621
Homology inference
Let $\mathbb{X}_n = \{x_1,...,x_n\}\subseteq \mathbb{R}^D$ be a finite sample.

Homology inference
Let $\mathbb{X}_n = \{x_1,...,x_n\}\subseteq \mathbb{R}^D$ be a finite sample.
Assume that:
- $\mathbb{X}_n$ is a sample of a compact Riemannian manifold $\mathcal M$ of dimension $d$.
- The points are sampled according to a density $f\colon \mathcal M\to \mathbb R$.
Goal: Infer $H_\bullet(\mathcal M)$

Homology inference
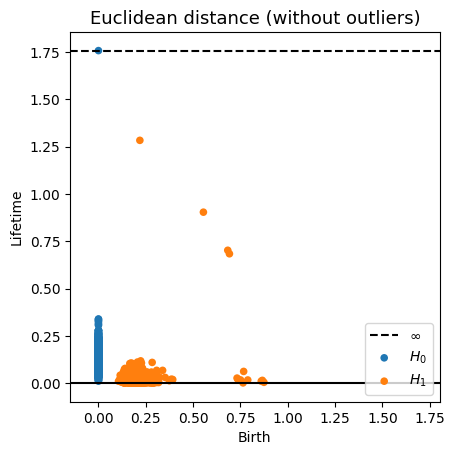
Euclidean distance Metric space: $(\mathbb X_n, d_E)\sim (\mathcal M, d_E)$
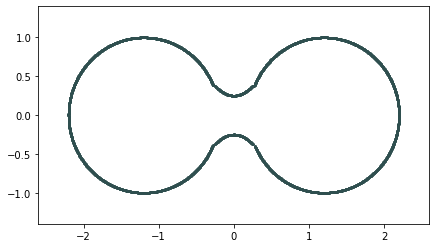

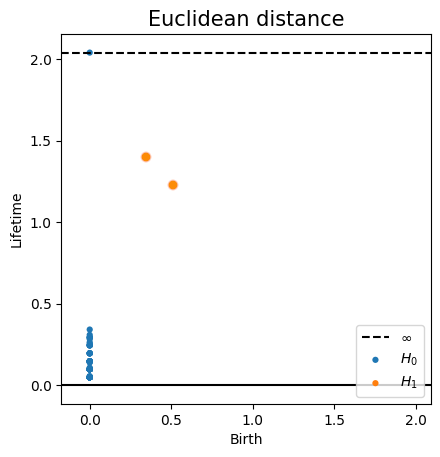
Homology inference
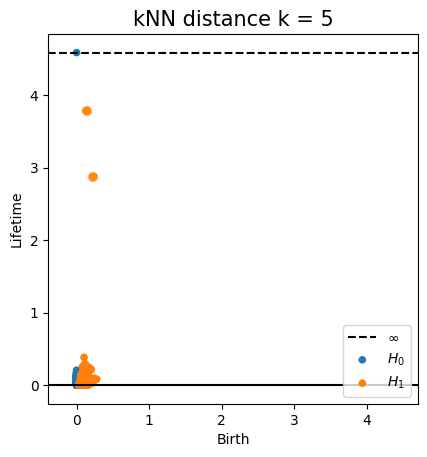
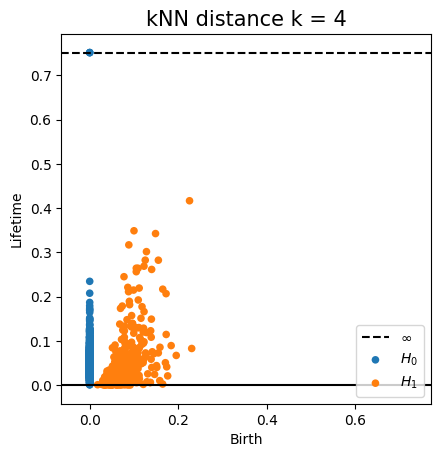
Metric space: $(\mathbb X_n, d_{kNN})\sim (\mathcal M, d_\mathcal{M})$

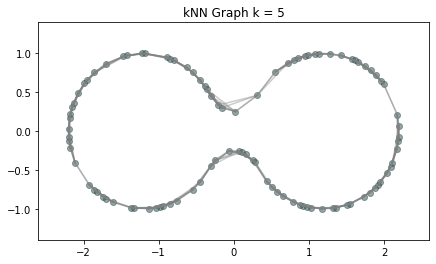
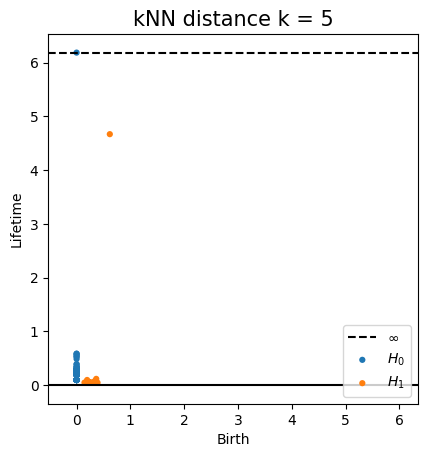
Homology inference
Metric space: $(\mathbb X_n, d_{kNN})\sim (\mathcal M, d_\mathcal{M})$

Homology inference
Metric space: $(\mathbb X_n, d_{kNN})\sim (\mathcal M, d_\mathcal{M})$



Homology inference
Metric space: $(\mathbb X_n, d_{kNN})\sim (\mathcal M, d_\mathcal{M})$


Fermat distance
Let $\mathbb{X}_n = \{x_1,...,x_n\}\subseteq \mathbb{R}^D$ be a finite sample.
For $p> 1$, the Fermat distance between $x,y\in \mathbb{R}^D$ is defined by \[ d_{\mathbb{X}_n, p}(x,y) = \inf_{\gamma} \sum_{i=0}^{r}|x_{i+1}-x_i|^{p} \] over all paths $\gamma=(x_0, \dots, x_{r+1})$ of finite length with $x_0=x$, $x_{r+1} = y$ and $\{x_1, x_2, \dots, x_{r}\}\subseteq \mathbb{X}_n$.
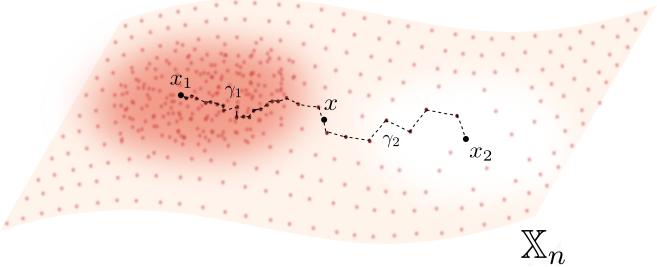
Fermat distance
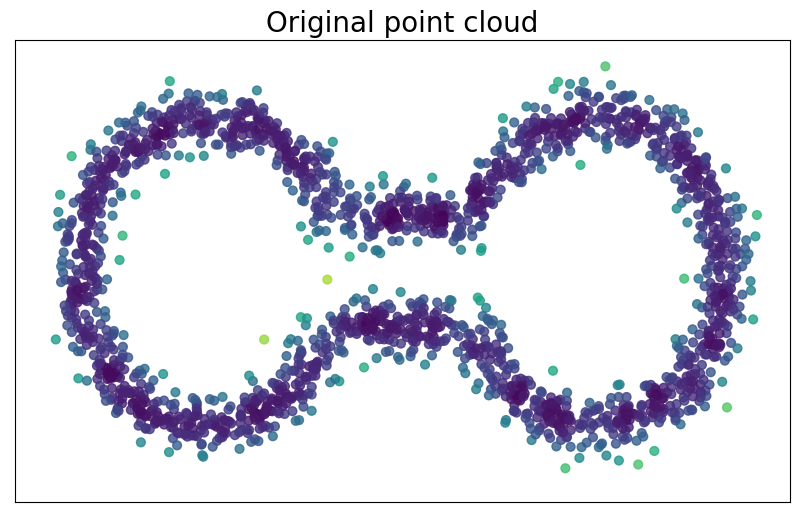
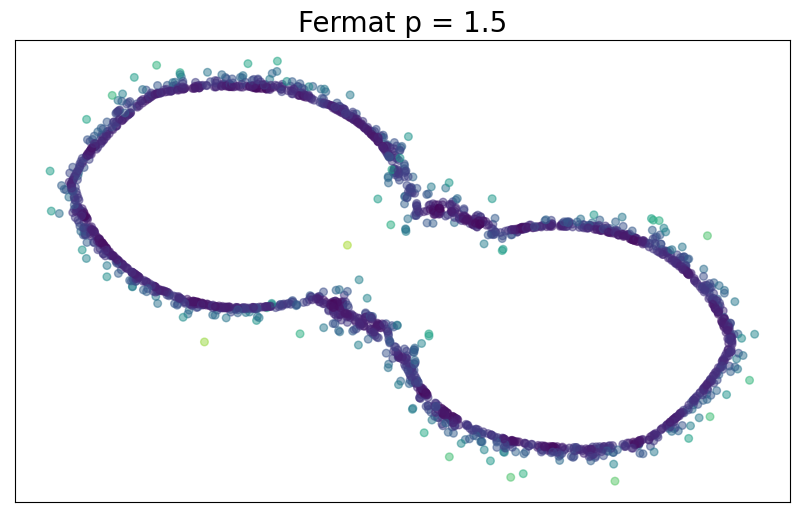
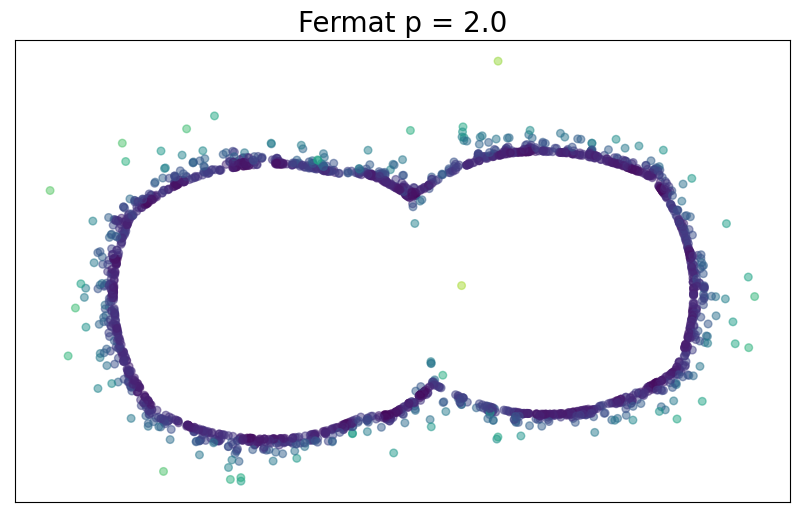
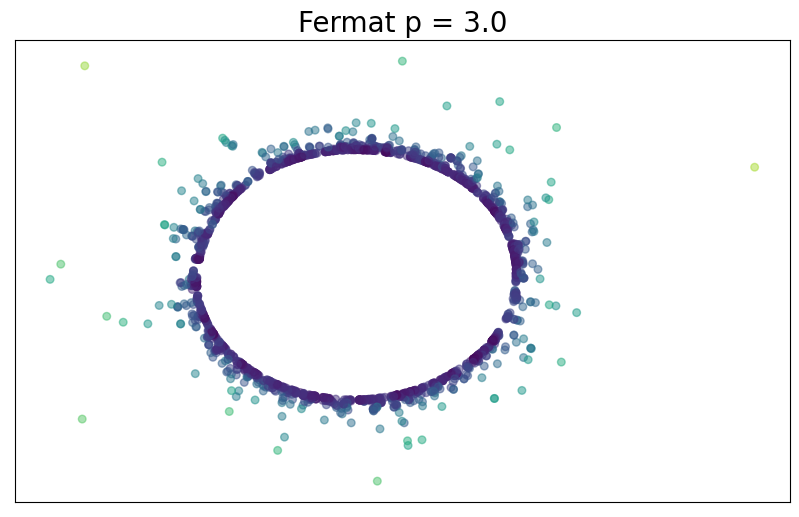
Density-based riemmanian geometry
Let $\mathcal M \subseteq \mathbb{R}^D$ be a manifold and let $f:\mathcal{M}\to \mathbb{R}_{>0}$ be a smooth density.
For $q>0$, the deformed Riemannian distance in $\mathcal{M}$ is \[ d_{f,q}(x,y) = \inf_{\gamma} \int_{\gamma}\frac{1}{f(\gamma)^{q}} \] over all $\gamma:I\to \mathcal{M}$ with $\gamma(0) = x$ and $\gamma(1)=y$.
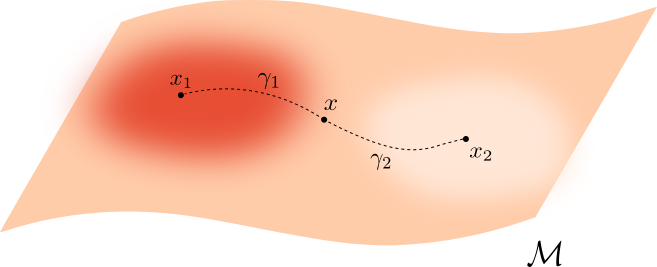
Properties of Fermat distance
Convergence of metric spaces
\[\big(\mathbb{X}_n, C(n,p,d) d_{\mathbb{X}_n,p})\big)\xrightarrow[n\to \infty]{GH}\big(\mathcal{M}, d_{f,q}\big) ~~~ \text{ for } q = (p-1)/d\]
Theorem (Borghini, F., Groisman, Mindlin)
Let $\mathcal{M}$ be a closed smooth $d$-dimensional Riemannian manifold embedded in $\mathbb{R}^D$. Let $\mathbb X_n\subseteq \mathcal{M}$ be a set of $n$ independent sample points with common smooth density $f:\mathcal{M}\to \mathbb{R}_{>0}$.
Given $p>1$ and $q=(p-1)/d$, there exists a constant $\mu = \mu(p,d)$ such that for every $\lambda \in \big((p-1)/pd, 1/d\big)$ and $\varepsilon>0$ there exist $\theta>0$ satisfying \[ \mathbb{P}\left( d_{GH}\left(\big(\mathcal{M}, d_{f,q}\big), \big(\mathbb{X}_n, {\scriptstyle \frac{n^{q}}{\mu}} d_{\mathbb{X}_n, p}\big)\right) > \varepsilon \right) \leq \exp{\left(-\theta n^{(1 - \lambda d) /(d+2p)}\right)} \] for $n$ large enough.
Properties of Fermat distance
Convergence of persistent diagrams
\[\mathrm{dgm}(\mathrm{Filt}(\mathbb{X}_n, {C(n,p,d)} d_{\mathbb{X}_n,p}))\xrightarrow[n\to \infty]{B}\mathrm{dgm}(\mathrm{Filt}(\mathcal{M}, d_{f,q})) ~~~ \text{ for } q = (p-1)/d\]
Corollary (Borghini, F., Groisman, Mindlin)
Let $\mathcal{M}$ be a closed smooth $d$-dimensional Riemannian manifold embedded in $\mathbb{R}^D$. Let $\mathbb X_n\subseteq \mathcal{M}$ be a set of $n$ independent sample points with common smooth density $f:\mathcal{M}\to \mathbb{R}_{>0}$.
Given $p>1$ and $q=(p-1)/d$, there exists a constant $\mu = \mu(p,d)$ such that for every $\lambda \in \big((p-1)/pd, 1/d\big)$ and $\varepsilon>0$ there exist $\theta>0$ satisfying \[ \mathbb{P}\Big( d_B\big(\mathrm{dgm}(\mathrm{Filt}(\mathcal{M}, d_{f,q})),\mathrm{dgm}(\mathrm{Filt}(\mathbb{X}_n, {\scriptstyle \frac{n^{q}}{\mu}} d_{\mathbb{X}_n,p}))\big)>\varepsilon\Big)\\\leq \exp{\big(-\theta n^{(1 - \lambda d)/(d+2p)}\big)}\] for $n$ large enough.
Density-based intrinsic persistence diagrams

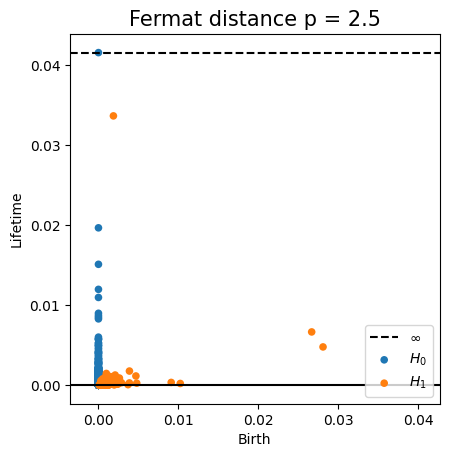
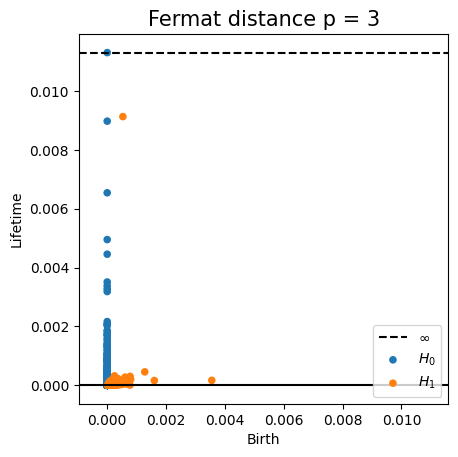
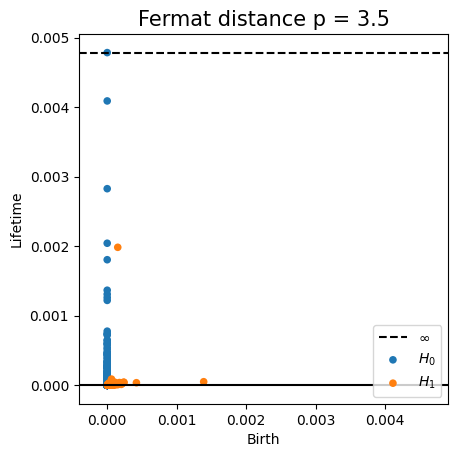
Properties of Fermat distance
Robustness to outliers
Prop (Borghini, F., Groisman, Mindlin)
Let $\mathbb{X}_n$ be a sample of $\mathcal{M}$ and let $Y\subseteq \mathbb{R}^D\smallsetminus \mathcal{M}$ be a finite set of outliers. There exists $\delta >0$ such that for all $k>0$ and $p>1$, \[ \mathrm{dgm}_k(\mathrm{Rips}_{<\delta^p}(\mathbb{X}_n \cup Y, d_{\mathbb{X}_n\cup Y, p})) = \mathrm{dgm}_k(\mathrm{Rips}_{<\delta^p}(\mathbb{X}_n, d_{\mathbb{X}_n, p})) \] where $\mathrm{Rips}_{<\delta^p}$ stands for the Rips filtration up to parameter $\delta^{p}$ and $\mathrm{dgm}_k$ for the persistent homology of deg $k$.
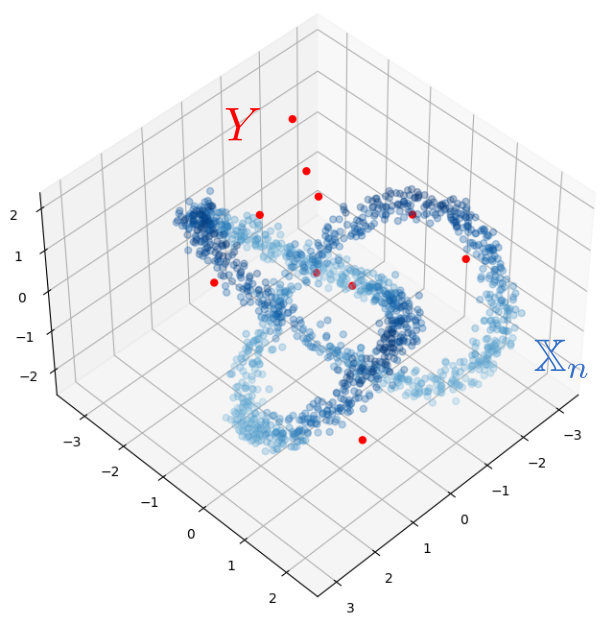
Properties of Fermat distance
Robustness to outliers
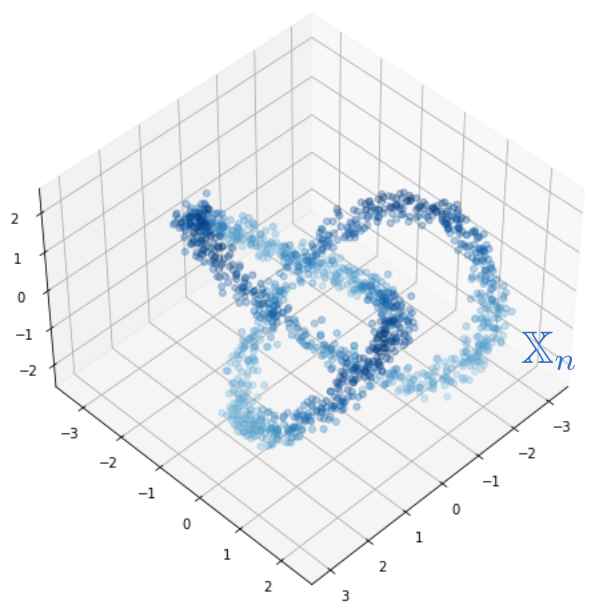
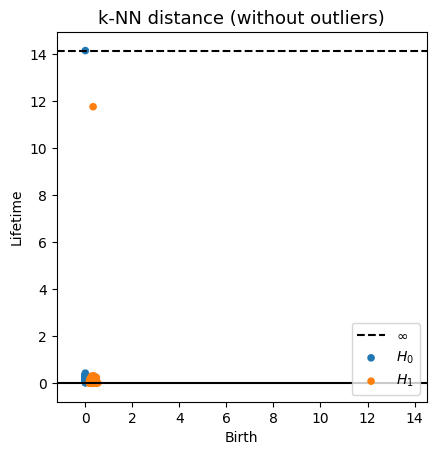
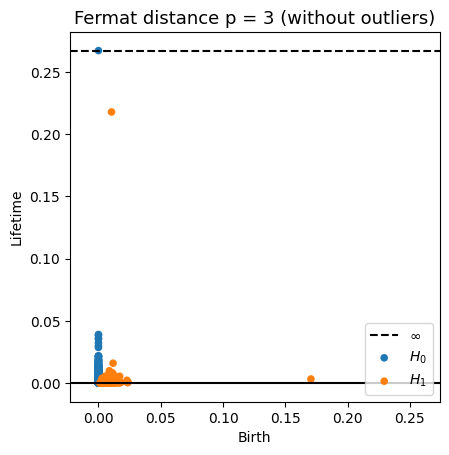

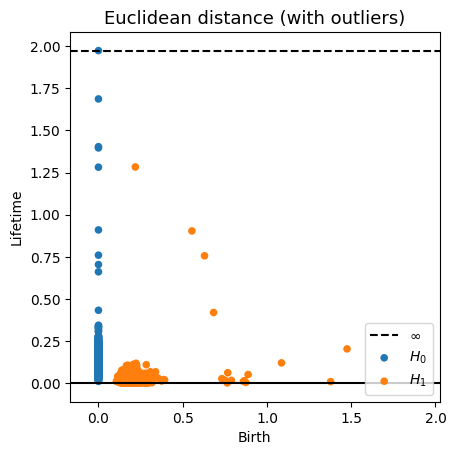
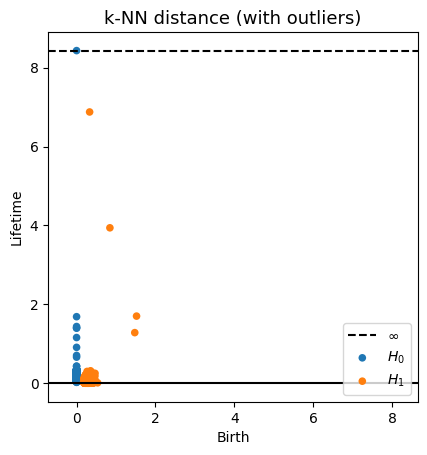
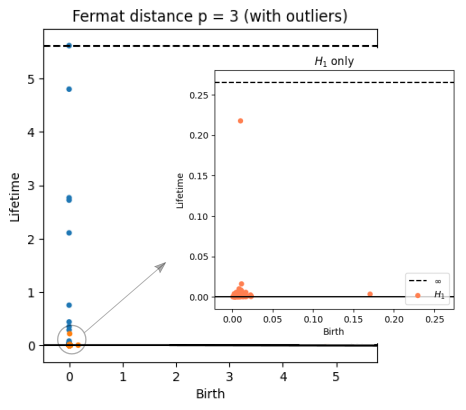
Fermat distance
Computational implementation
- Complexity:
$O(n^3)$
reducible to $O(n^2*k*\log(n))$ using the $k$-NN-graph (for $k = O(\log n)$ the geodesics belong to the $k$-NN graph with high probability).
- Python library:
fermat
- Tool in Giotto-TDA:
Coming soon :)
- Computational experiments:
ximenafernandez/intrinsicPH
Applications to time series analysis
$\bullet$ Fernandez X., Borghini E., Mindlin G., Groisman P. Intrinsic persistent homology via density-based metric learning, 2021. arXiv:2012.07621
$\bullet$ Fernandez X., Mateos D. Topological prediction of epileptic seizures. Work in progress, 2021.
Delay embedding
- Signal:
$X:[t_0,t_1] \to \mathbb{R}$
- Delay embedding: Given $T$ the time delay and $D$ the embedding dimension. \[\mathcal{M}_{[t_0, t_1]} = \{\big(X(t), X(t+T), X(t+2 T) \dots, X(t+(D-1)T)\big): t\in [t_0, t_1-(D-1)T]\}\subseteq \mathbb{R}^D\]
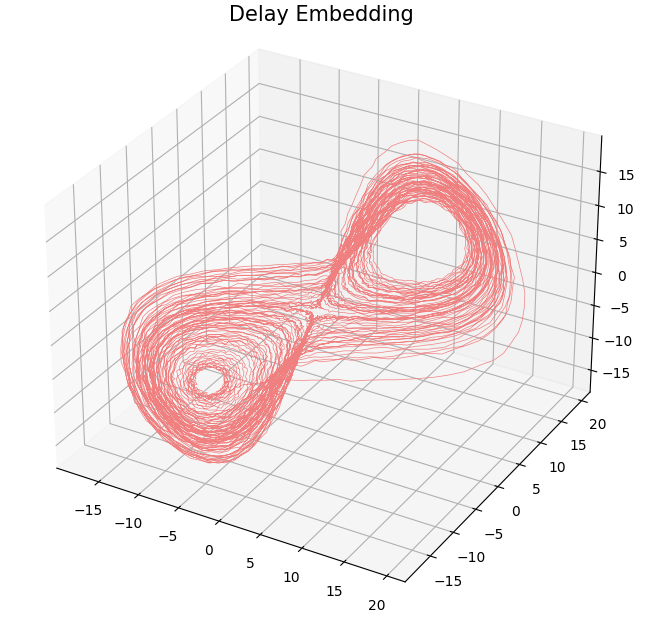
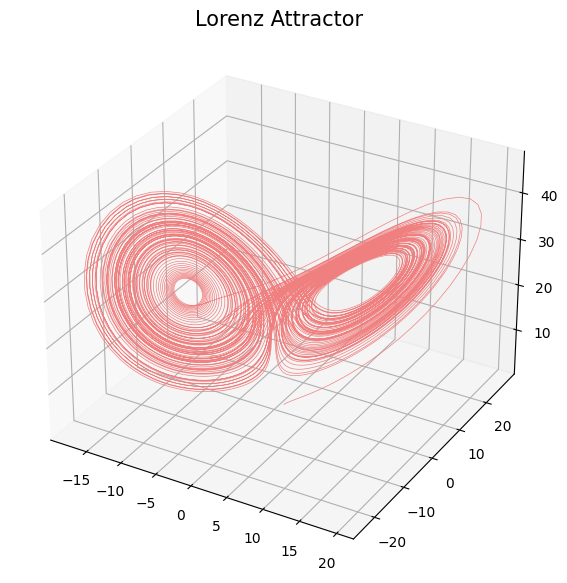
Anomaly detection
Electrocardiogram
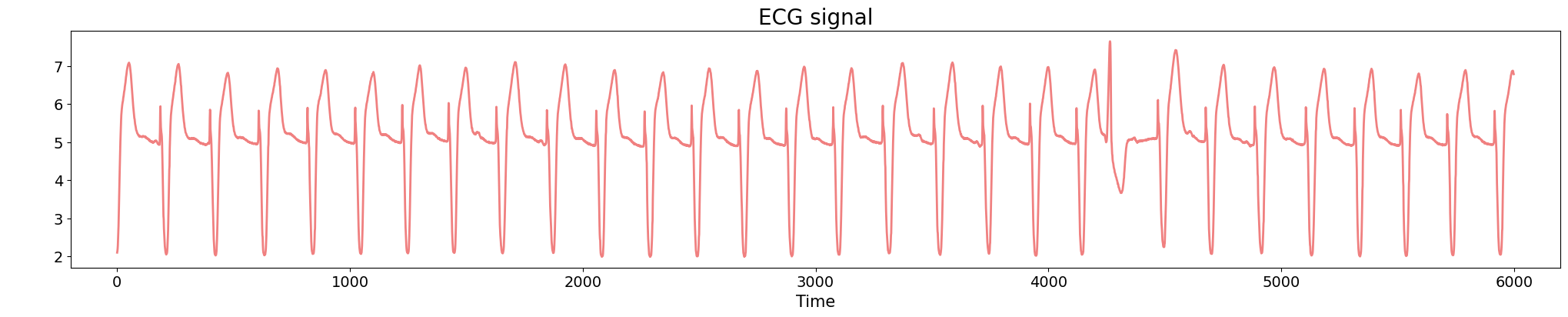
Source data: PhysioNet Database https://physionet.org/about/database/
Anomaly detection
Electrocardiogram

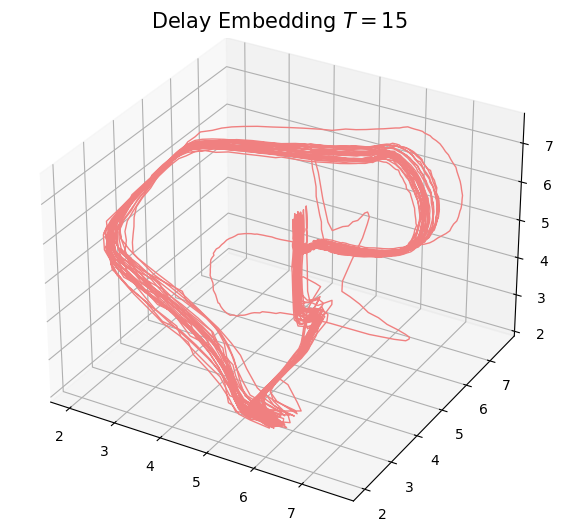
Anomaly detection
Electrocardiogram
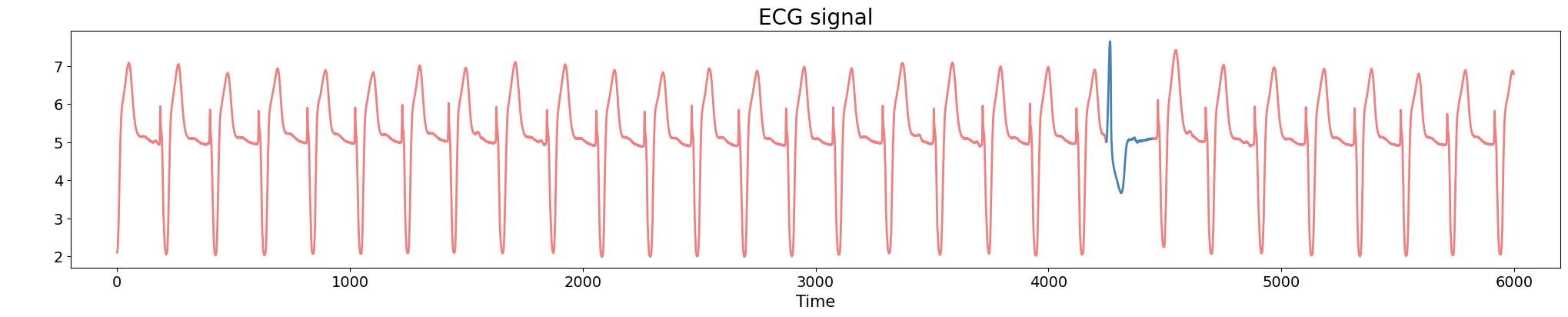
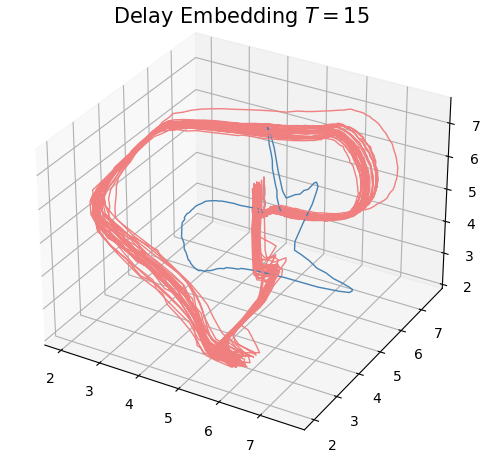
Anomaly detection
Electrocardiogram


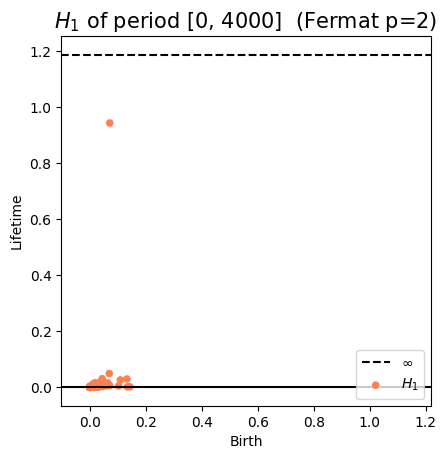
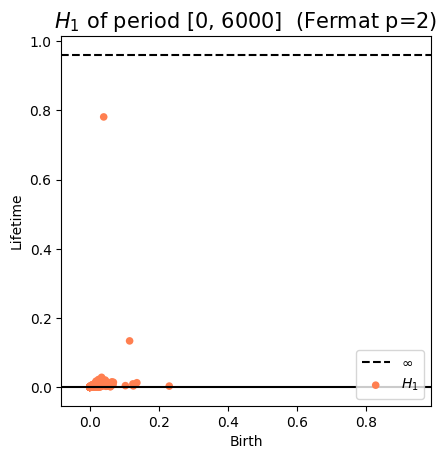
Anomaly detection
Electrocardiogram
 \[t\mapsto \mathbb{dgm_1}(\mathrm{Rips}(\mathcal M_{T, D}[0,t]))\]
\[t\mapsto \mathbb{dgm_1}(\mathrm{Rips}(\mathcal M_{T, D}[0,t]))\]
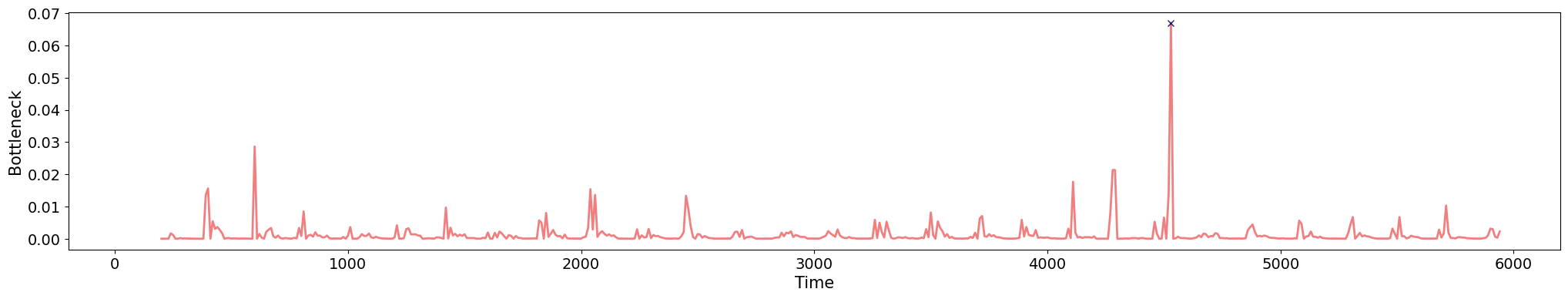
Change-points detection
Birdsongs
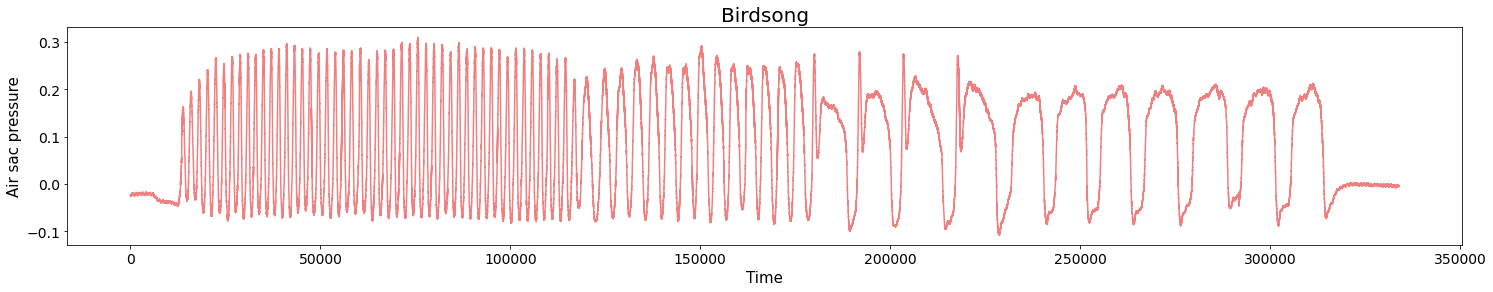
Source data: Private experiments. Laboratory of Dynamical Systems, University of Buenos Aires.
Change-points detection
Birdsongs

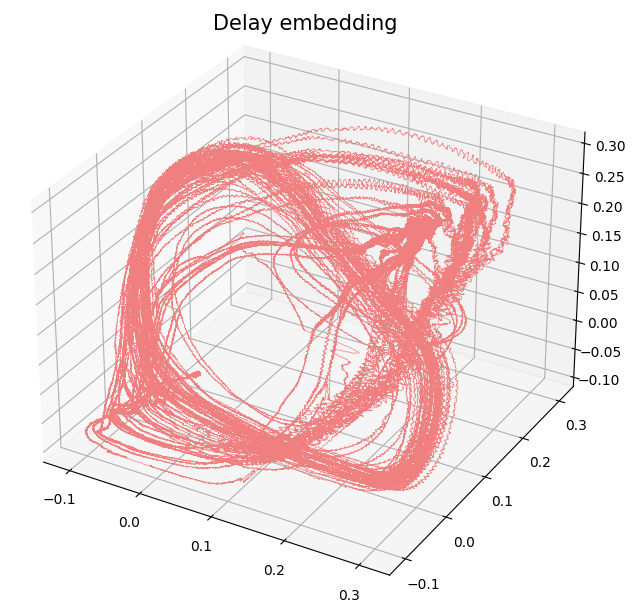
Change-points detection
Birdsongs


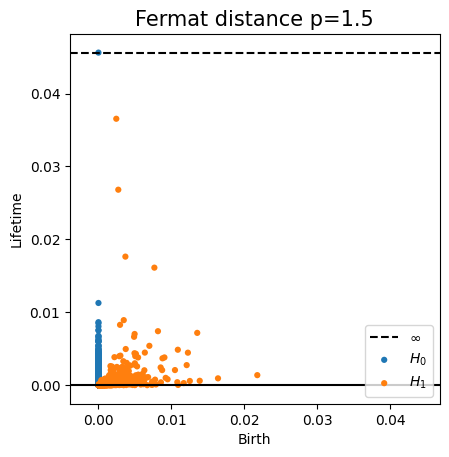
Change-points detection
Birdsongs
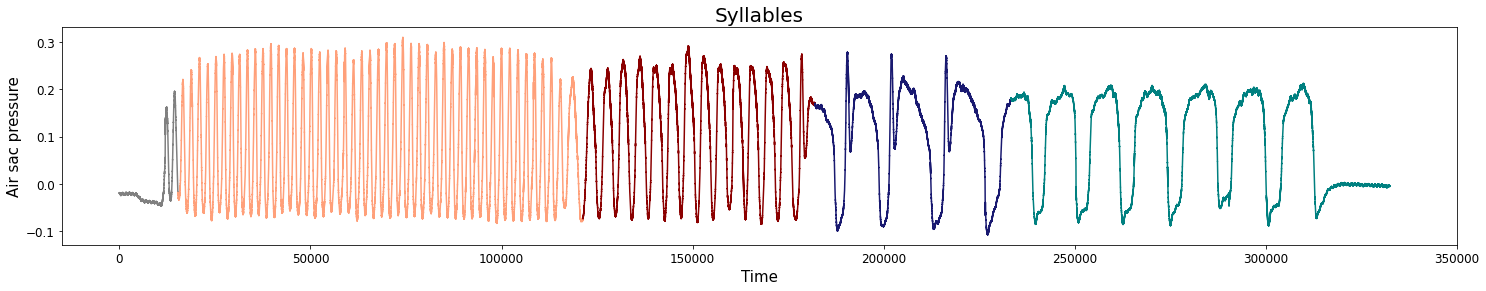
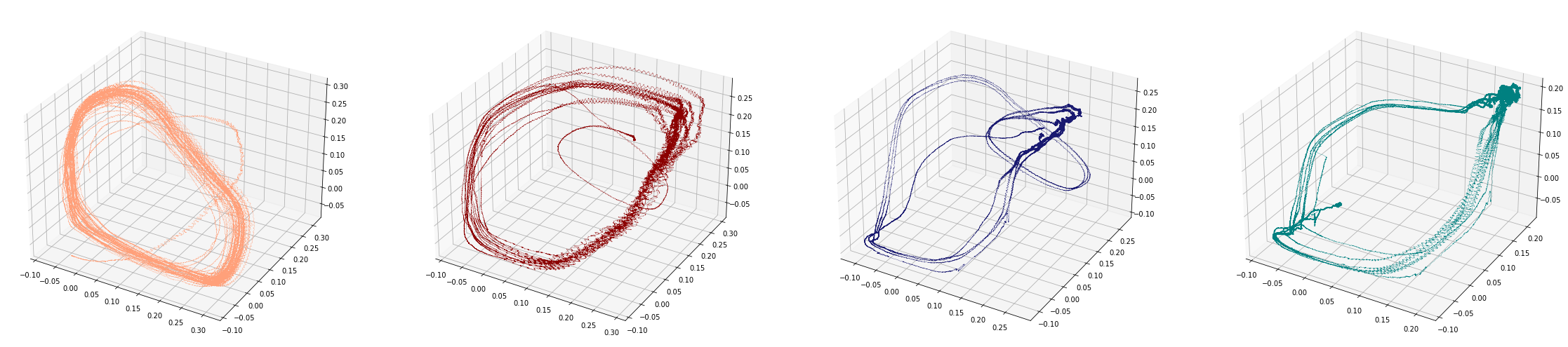

Change-points detection
Birdsongs
 \[t\mapsto \mathbb{dgm_1}(\mathrm{Rips}(\mathcal M_{T, D}[0,t]))\]
\[t\mapsto \mathbb{dgm_1}(\mathrm{Rips}(\mathcal M_{T, D}[0,t]))\]
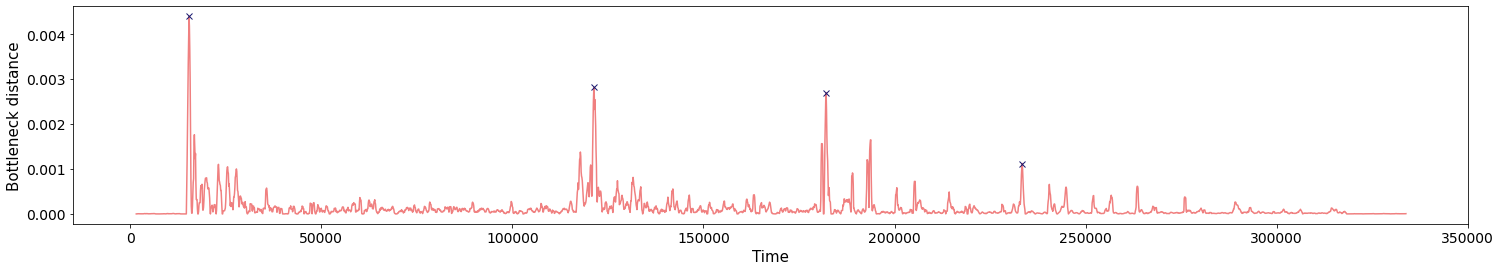
Prediction of transitions
Electroencefalogram
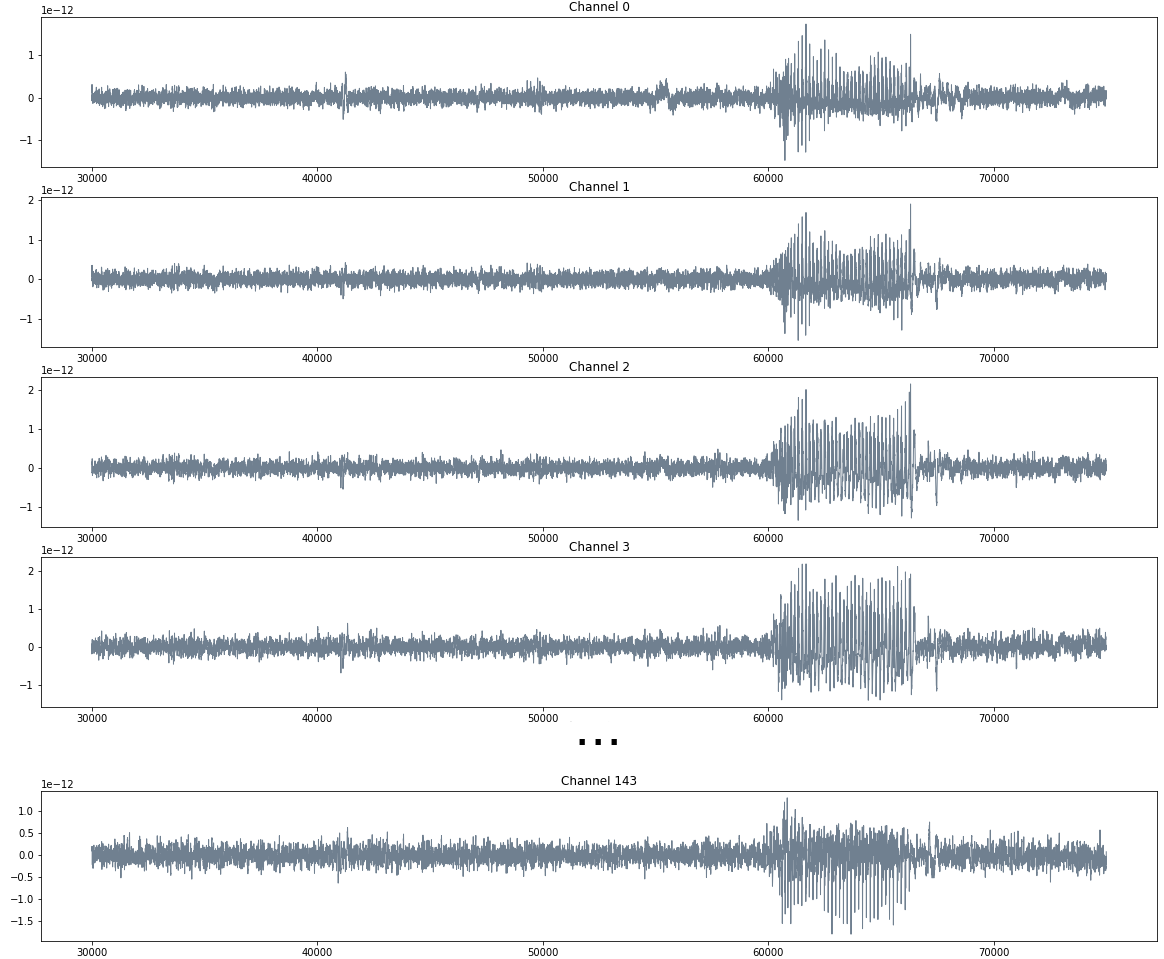
Source data: Private experiments. Institute of Applied Math of Litoral (IMAL-CONICET-UNL).
Prediction of transitions
Electroencefalogram
 $W$ size of the restricted interval.
\[t\mapsto \mathbb{dgm_1}(\mathrm{Rips}((f_0, \dots, f_{143})[t-W,t]))\]
$W$ size of the restricted interval.
\[t\mapsto \mathbb{dgm_1}(\mathrm{Rips}((f_0, \dots, f_{143})[t-W,t]))\]

Thanks!